元素在可视区域中
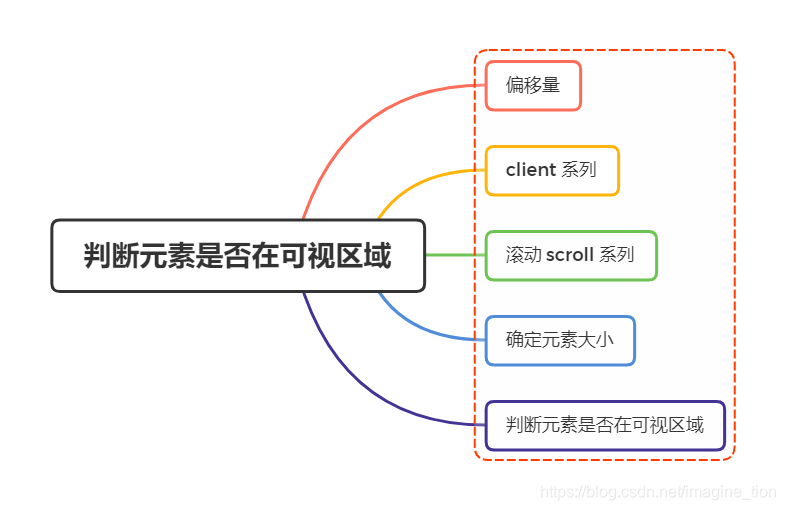
偏移量#
| 偏移量 | 概念 | 公式 |
|---|---|---|
| offsetHeight | 元素在垂直方向上占用的空间大小,以像素为单位。包括元素的高度、(可见的) 水平滚动条的高度、上下边框高度 | offsetHeght = content + padding + border + scrollX |
| offsetWidth | 元素在水平方向上占用的空间大小,以像素为单位。包括元素的宽度、(可见的)垂直滚动条的宽度、左右边框宽度 | offsetWidth = content + padding + border + scrollY |
| offsetLeft | 元素的左外边框距离与已定位的父容器(offsetParent)的左边距离(不包括元素的边框和父容器的边框) | |
| offsetTop | 元素的上外边框距离与已定位的父容器的上边距离(不包括元素的边框和父容器的边框) |
如下图:
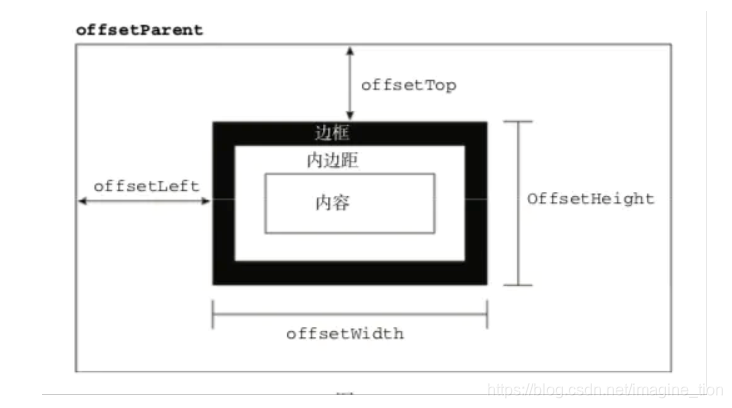
小结:
- 只读属性
- 包括滚动条和边框,不包括外边距
- 每次访问都要重新计算(用变量进行保存)
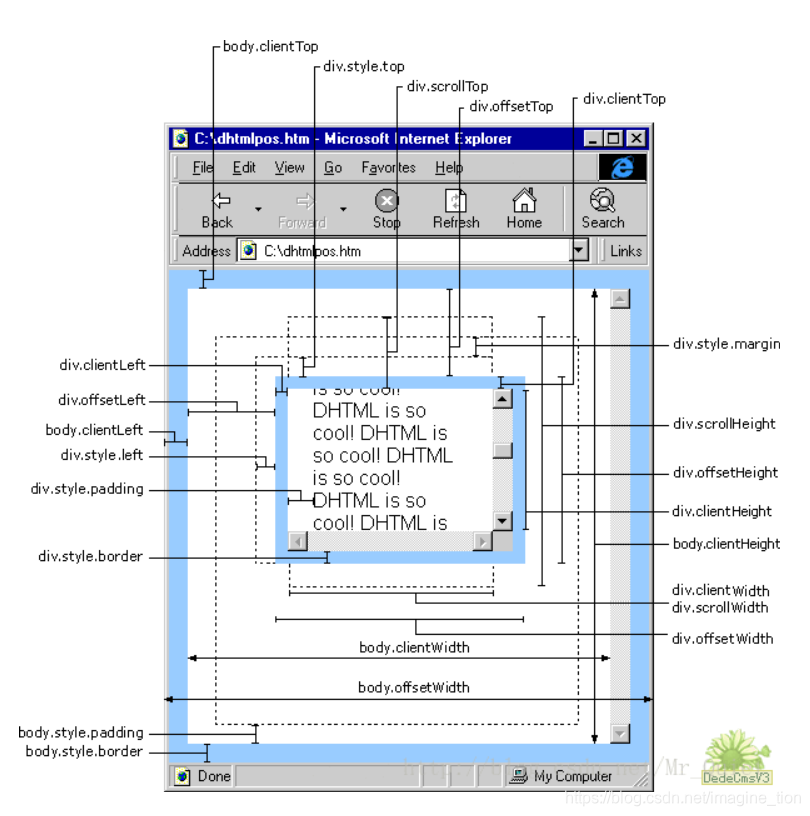
client 系列#
| 客户区大小 | 概念 | 公式 |
|---|---|---|
| clientWidth | clientWidth 属性是元素内容区宽度加上左右内边距宽度,不包括滚动条、边框和外边距 | clientWidth = content + padding |
| clientHeight | 元素内容区高度加上上下内边距高度,不包括滚动条、边框和外边距 | clientHeight = content + padding |
| clientLeft | 实际上就是左边框宽度 | clientLeft = border-left |
| clientTop | 实际上就是上边框宽度 | clientLeft = border-top |
常用于获取浏览器视口大小
小结:
- 只读属性
- 每次访问都要重新计算(用变量进行保存)
滚动 scroll 系列#
| 滚动大小 | 概念 |
|---|---|
| scrollWidth | 在没有滚动条的情况下,元素内容的总高度 |
| scrollHeight | 在没有滚动条的情况下,元素内容的总宽度 |
| scrollLeft | 被隐藏在内容区域左侧的像素数。通过设置这个属性可以改变元素的滚动位置 |
| scrollTop | 被隐藏在内容区域上方的像素数。通过设置这个属性可以改变元素的滚动位置 |
scrollWidth和scrollHeight主要用于确定元素内容的实际大小scrollLeft和scrollTop属性既可以确定元素当前滚动的状态,也可以设置元素的滚动位置- 垂直滚动
scrollTop > 0 - 水平滚动
scrollLeft > 0
- 垂直滚动
- 将元素的
scrollLeft和scrollTop设置为 0,可以重置元素的滚动位置
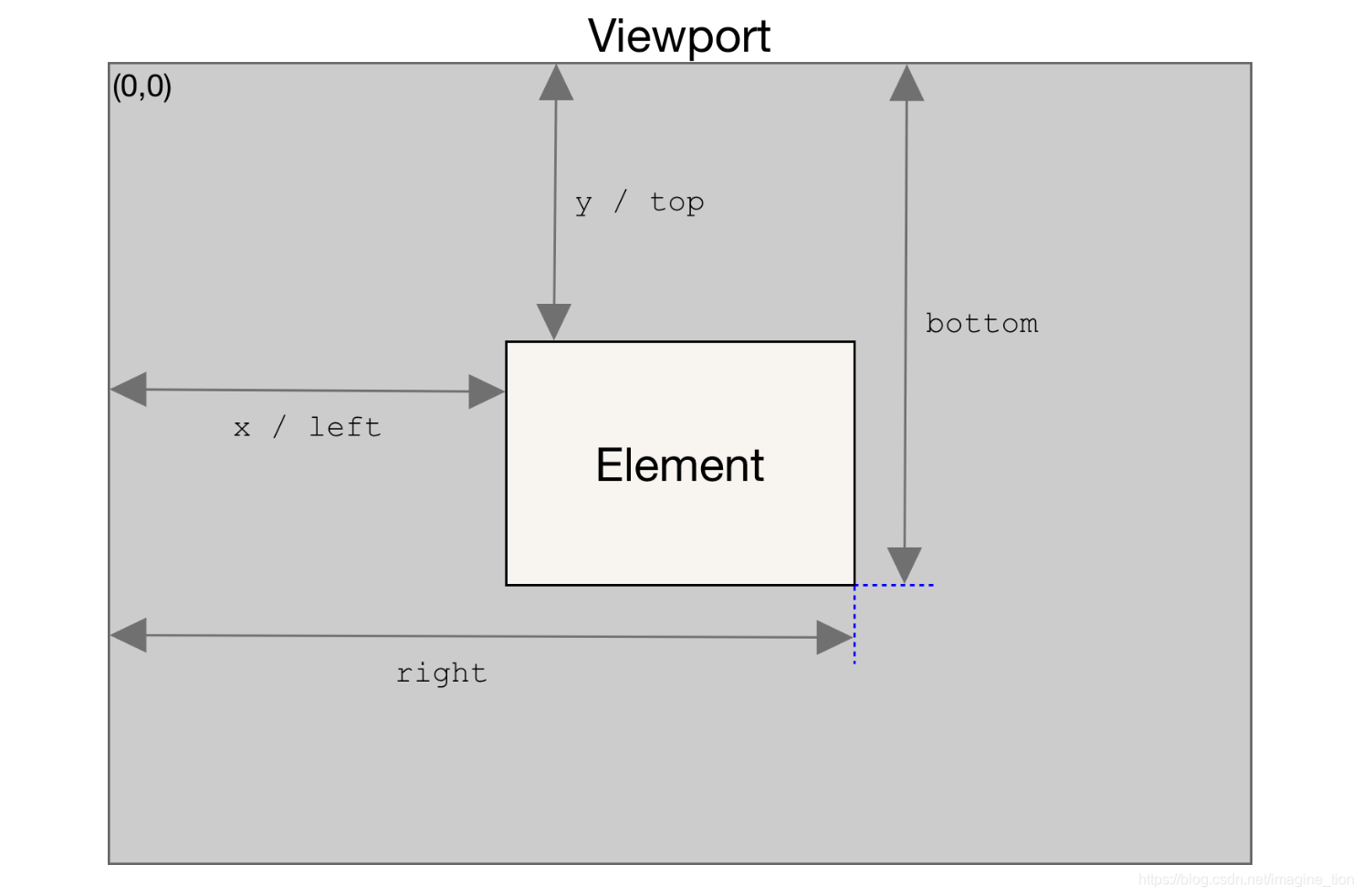
确定元素大小#
Element.getBoundingClientRect()方法返回一个DOMRect对象,该对象提供有关元素大小及其相对于视口的位置的信息
这个方法返回一个矩形对象,含4个属性:left、top、right 和 bottom 。这些属性给出了元素在页面中相对于视口的位置
- top:元素上边到视窗上边的距离
- right:元素右边到视窗左边的距离
- bottom:元素下边到视窗上边的距离
- left:元素左边到视窗左边的距离
对于不支持 getBoundingClientRect() 的浏览器,可以通过其他手段取得相同的信息。一般来说,right 和 left 的差值与 offsetWidth 的值相等,而 bottom 和 top 的差值与 offsetHeight 相等
判断元素是否在可视区域#
第一种方法#
el.offsetTop - document.documentElement.scrollTop <= viewPortHeight
第二种方法#
el.getBoundingClientReact().top <= viewPortHeight
第三种方法#
intersectionRatio > 0 && intersectionRatio <= 1